線性混合效應模型¶
[1]:
%matplotlib inline
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import statsmodels.api as sm
import statsmodels.formula.api as smf
from statsmodels.tools.sm_exceptions import ConvergenceWarning
注意:此筆記本中的 R 程式碼和結果已轉換為 markdown,因此不需要 R 來建構文件。筆記本中的 R 結果是使用 R 3.5.1 和 lme4 1.1 計算得出的。
%load_ext rpy2.ipython
%R library(lme4)
array(['lme4', 'Matrix', 'tools', 'stats', 'graphics', 'grDevices',
'utils', 'datasets', 'methods', 'base'], dtype='<U9')
比較 R lmer 與 statsmodels MixedLM¶
statsmodels 線性混合模型 (MixedLM) 的實作,緊密遵循 Lindstrom 和 Bates (JASA 1988) 中概述的方法。這也是 R 套件 LME4 中採用的方法。其他套件,如 Stata、SAS 等,也應與此方法一致,因為該領域的基本技術大多已成熟。
在這裡,我們展示如何使用 statsmodels 中的 MixedLM 程序擬合線性混合模型。包含來自 R (LME4) 的結果以供比較。
以下是我們的導入語句
豬隻的生長曲線¶
這些是來自因子實驗的縱向資料。結果變數是每隻豬的體重,我們在這裡使用的唯一預測變數是「時間」。首先,我們擬合一個將平均體重表示為時間的線性函數的模型,每隻豬有一個隨機截距。該模型使用公式指定。由於未指定隨機效應結構,因此自動使用預設隨機效應結構(每組的隨機截距)。
[2]:
data = sm.datasets.get_rdataset("dietox", "geepack").data
md = smf.mixedlm("Weight ~ Time", data, groups=data["Pig"])
mdf = md.fit(method=["lbfgs"])
print(mdf.summary())
Mixed Linear Model Regression Results
========================================================
Model: MixedLM Dependent Variable: Weight
No. Observations: 861 Method: REML
No. Groups: 72 Scale: 11.3669
Min. group size: 11 Log-Likelihood: -2404.7753
Max. group size: 12 Converged: Yes
Mean group size: 12.0
--------------------------------------------------------
Coef. Std.Err. z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]
--------------------------------------------------------
Intercept 15.724 0.788 19.952 0.000 14.179 17.268
Time 6.943 0.033 207.939 0.000 6.877 7.008
Group Var 40.395 2.149
========================================================
這是使用 LMER 在 R 中擬合的相同模型
%%R
data(dietox, package='geepack')
%R print(summary(lmer('Weight ~ Time + (1|Pig)', data=dietox)))
Linear mixed model fit by REML ['lmerMod']
Formula: Weight ~ Time + (1 | Pig)
Data: dietox
REML criterion at convergence: 4809.6
Scaled residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-4.7118 -0.5696 -0.0943 0.4877 4.7732
Random effects:
Groups Name Variance Std.Dev.
Pig (Intercept) 40.39 6.356
Residual 11.37 3.371
Number of obs: 861, groups: Pig, 72
Fixed effects:
Estimate Std. Error t value
(Intercept) 15.72352 0.78805 19.95
Time 6.94251 0.03339 207.94
Correlation of Fixed Effects:
(Intr)
Time -0.275
請注意,在 statsmodels 的結果摘要中,固定效應和隨機效應的參數估計值顯示在單個表格中。動物的隨機效應在上面的 statsmodels 輸出中標記為「截距 RE」。在 LME4 輸出中,此效應是隨機效應部分下的豬截距。
關於隨機效應變異數和共變異數參數的標準誤差是否有用,一直存在很多爭論。在 LME4 中,這些標準誤差不會顯示,因為套件的作者認為它們沒有太多參考價值。雖然有充分的理由質疑它們的實用性,但我們選擇在摘要表格中包含標準誤差,但不顯示相應的 Wald 信賴區間。
接下來,我們擬合一個模型,每隻動物有兩個隨機效應:一個隨機截距和一個隨機斜率(相對於時間)。這意味著每隻豬可能具有不同的基準體重,並且以不同的速率生長。公式指定「時間」是具有隨機係數的共變數。預設情況下,公式始終包含截距(可以使用「0 + 時間」作為公式在此處抑制)。
[3]:
md = smf.mixedlm("Weight ~ Time", data, groups=data["Pig"], re_formula="~Time")
mdf = md.fit(method=["lbfgs"])
print(mdf.summary())
Mixed Linear Model Regression Results
===========================================================
Model: MixedLM Dependent Variable: Weight
No. Observations: 861 Method: REML
No. Groups: 72 Scale: 6.0372
Min. group size: 11 Log-Likelihood: -2217.0475
Max. group size: 12 Converged: Yes
Mean group size: 12.0
-----------------------------------------------------------
Coef. Std.Err. z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]
-----------------------------------------------------------
Intercept 15.739 0.550 28.603 0.000 14.660 16.817
Time 6.939 0.080 86.925 0.000 6.783 7.095
Group Var 19.503 1.561
Group x Time Cov 0.294 0.153
Time Var 0.416 0.033
===========================================================
這是使用 R 中的 LMER 擬合的相同模型
%R print(summary(lmer("Weight ~ Time + (1 + Time | Pig)", data=dietox)))
Linear mixed model fit by REML ['lmerMod']
Formula: Weight ~ Time + (1 + Time | Pig)
Data: dietox
REML criterion at convergence: 4434.1
Scaled residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-6.4286 -0.5529 -0.0416 0.4841 3.5624
Random effects:
Groups Name Variance Std.Dev. Corr
Pig (Intercept) 19.493 4.415
Time 0.416 0.645 0.10
Residual 6.038 2.457
Number of obs: 861, groups: Pig, 72
Fixed effects:
Estimate Std. Error t value
(Intercept) 15.73865 0.55012 28.61
Time 6.93901 0.07982 86.93
Correlation of Fixed Effects:
(Intr)
Time 0.006
隨機截距和隨機斜率僅有微弱的相關性 \((0.294 / \sqrt{19.493 * 0.416} \approx 0.1)\)。因此,接下來我們擬合一個模型,其中兩個隨機效應被約束為不相關
[4]:
0.294 / (19.493 * 0.416) ** 0.5
[4]:
0.10324316832591753
[5]:
md = smf.mixedlm("Weight ~ Time", data, groups=data["Pig"], re_formula="~Time")
free = sm.regression.mixed_linear_model.MixedLMParams.from_components(
np.ones(2), np.eye(2)
)
mdf = md.fit(free=free, method=["lbfgs"])
print(mdf.summary())
Mixed Linear Model Regression Results
===========================================================
Model: MixedLM Dependent Variable: Weight
No. Observations: 861 Method: REML
No. Groups: 72 Scale: 6.0283
Min. group size: 11 Log-Likelihood: -2217.3481
Max. group size: 12 Converged: Yes
Mean group size: 12.0
-----------------------------------------------------------
Coef. Std.Err. z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]
-----------------------------------------------------------
Intercept 15.739 0.554 28.388 0.000 14.652 16.825
Time 6.939 0.080 86.248 0.000 6.781 7.097
Group Var 19.837 1.571
Group x Time Cov 0.000 0.000
Time Var 0.423 0.033
===========================================================
當我們將相關參數固定為 0 時,對數概似下降 0.3。將 2 x 0.3 = 0.6 與卡方 1 自由度參考分佈進行比較,表明資料與該參數等於 0 的模型非常一致。
這是使用 R 中的 LMER 擬合的相同模型(請注意,此處 R 報告的是 REML 準則而不是對數概似,其中 REML 準則是對數概似的兩倍)
%R print(summary(lmer("Weight ~ Time + (1 | Pig) + (0 + Time | Pig)", data=dietox)))
Linear mixed model fit by REML ['lmerMod']
Formula: Weight ~ Time + (1 | Pig) + (0 + Time | Pig)
Data: dietox
REML criterion at convergence: 4434.7
Scaled residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-6.4281 -0.5527 -0.0405 0.4840 3.5661
Random effects:
Groups Name Variance Std.Dev.
Pig (Intercept) 19.8404 4.4543
Pig.1 Time 0.4234 0.6507
Residual 6.0282 2.4552
Number of obs: 861, groups: Pig, 72
Fixed effects:
Estimate Std. Error t value
(Intercept) 15.73875 0.55444 28.39
Time 6.93899 0.08045 86.25
Correlation of Fixed Effects:
(Intr)
Time -0.086
西特卡雲杉生長資料¶
這是 LMER R 函式庫中提供的範例資料集之一。結果變數是樹木的大小,這裡使用的共變數是時間值。資料按樹木分組。
[6]:
data = sm.datasets.get_rdataset("Sitka", "MASS").data
endog = data["size"]
data["Intercept"] = 1
exog = data[["Intercept", "Time"]]
這是 statsmodels LME 對具有隨機截距的基本模型的擬合。我們將 endog 和 exog 資料直接以陣列形式傳遞給 LME 初始化函式。另請注意,endog_re 在參數 4 中明確指定為隨機截距(儘管如果未指定,這也將是預設值)。
[7]:
md = sm.MixedLM(endog, exog, groups=data["tree"], exog_re=exog["Intercept"])
mdf = md.fit()
print(mdf.summary())
Mixed Linear Model Regression Results
=======================================================
Model: MixedLM Dependent Variable: size
No. Observations: 395 Method: REML
No. Groups: 79 Scale: 0.0392
Min. group size: 5 Log-Likelihood: -82.3884
Max. group size: 5 Converged: Yes
Mean group size: 5.0
-------------------------------------------------------
Coef. Std.Err. z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]
-------------------------------------------------------
Intercept 2.273 0.088 25.864 0.000 2.101 2.446
Time 0.013 0.000 47.796 0.000 0.012 0.013
Intercept Var 0.374 0.345
=======================================================
這是使用 LMER 在 R 中擬合的相同模型
%R
data(Sitka, package="MASS")
print(summary(lmer("size ~ Time + (1 | tree)", data=Sitka)))
Linear mixed model fit by REML ['lmerMod']
Formula: size ~ Time + (1 | tree)
Data: Sitka
REML criterion at convergence: 164.8
Scaled residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-2.9979 -0.5169 0.1576 0.5392 4.4012
Random effects:
Groups Name Variance Std.Dev.
tree (Intercept) 0.37451 0.612
Residual 0.03921 0.198
Number of obs: 395, groups: tree, 79
Fixed effects:
Estimate Std. Error t value
(Intercept) 2.2732443 0.0878955 25.86
Time 0.0126855 0.0002654 47.80
Correlation of Fixed Effects:
(Intr)
Time -0.611
我們現在可以嘗試加入隨機斜率。這次我們從 R 開始。從下面的程式碼和輸出中,我們看到隨機斜率的變異數的 REML 估計值幾乎為零。
%R print(summary(lmer("size ~ Time + (1 + Time | tree)", data=Sitka)))
Linear mixed model fit by REML ['lmerMod']
Formula: size ~ Time + (1 + Time | tree)
Data: Sitka
REML criterion at convergence: 153.4
Scaled residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-2.7609 -0.5173 0.1188 0.5270 3.5466
Random effects:
Groups Name Variance Std.Dev. Corr
tree (Intercept) 2.217e-01 0.470842
Time 3.288e-06 0.001813 -0.17
Residual 3.634e-02 0.190642
Number of obs: 395, groups: tree, 79
Fixed effects:
Estimate Std. Error t value
(Intercept) 2.273244 0.074655 30.45
Time 0.012686 0.000327 38.80
Correlation of Fixed Effects:
(Intr)
Time -0.615
convergence code: 0
Model failed to converge with max|grad| = 0.793203 (tol = 0.002, component 1)
Model is nearly unidentifiable: very large eigenvalue
- Rescale variables?
如果我們在預設情況下使用 statsmodels LME 執行此操作,我們會發現變異數估計值確實非常小,這會導致有關解位於參數空間邊界的警告。迴歸斜率與 R 非常一致,但概似值遠高於 R 返回的值。
[8]:
exog_re = exog.copy()
md = sm.MixedLM(endog, exog, data["tree"], exog_re)
mdf = md.fit()
print(mdf.summary())
/opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.10.15/x64/lib/python3.10/site-packages/statsmodels/regression/mixed_linear_model.py:2237: ConvergenceWarning: The MLE may be on the boundary of the parameter space.
warnings.warn(msg, ConvergenceWarning)
Mixed Linear Model Regression Results
===============================================================
Model: MixedLM Dependent Variable: size
No. Observations: 395 Method: REML
No. Groups: 79 Scale: 0.0264
Min. group size: 5 Log-Likelihood: -62.4834
Max. group size: 5 Converged: Yes
Mean group size: 5.0
---------------------------------------------------------------
Coef. Std.Err. z P>|z| [0.025 0.975]
---------------------------------------------------------------
Intercept 2.273 0.101 22.513 0.000 2.075 2.471
Time 0.013 0.000 33.888 0.000 0.012 0.013
Intercept Var 0.646 0.914
Intercept x Time Cov -0.001 0.003
Time Var 0.000 0.000
===============================================================
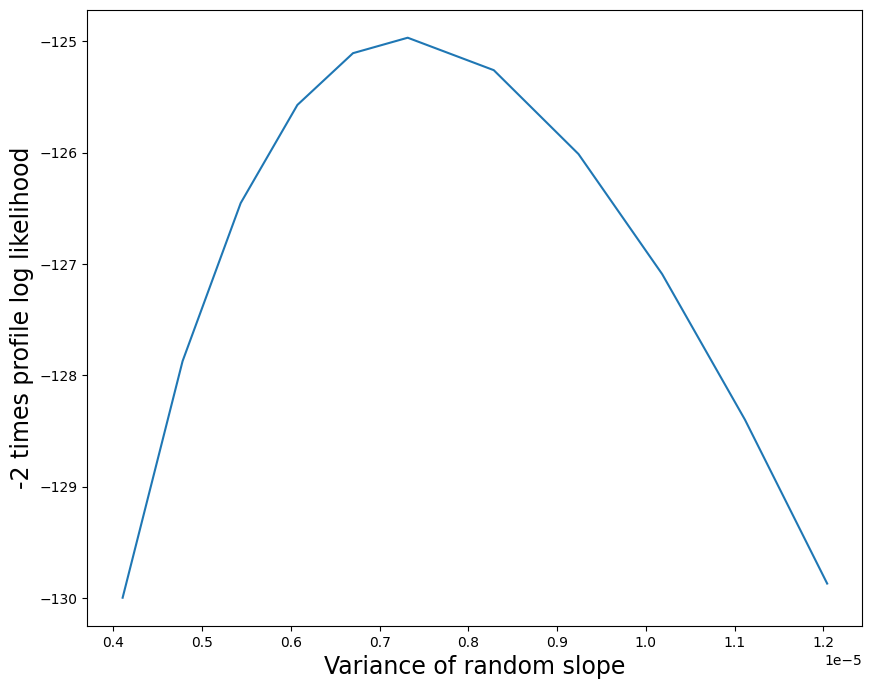
我們可以透過建構輪廓概似圖來進一步探索隨機效應結構。我們從隨機截距開始,產生一個輪廓概似圖,該圖從 MLE 下方 0.1 個單位到 MLE 上方 0.1 個單位。由於輪廓概似內部的每次最佳化都會產生警告(由於隨機斜率變異數接近於零),因此我們在此處關閉警告。
[9]:
import warnings
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
likev = mdf.profile_re(0, "re", dist_low=0.1, dist_high=0.1)
這是輪廓概似函式的圖。我們將對數概似差乘以 2 以獲得具有 1 個自由度的通常 \(\chi^2\) 參考分佈。
[10]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
[11]:
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
plt.plot(likev[:, 0], 2 * likev[:, 1])
plt.xlabel("Variance of random intercept", size=17)
plt.ylabel("-2 times profile log likelihood", size=17)
[11]:
Text(0, 0.5, '-2 times profile log likelihood')
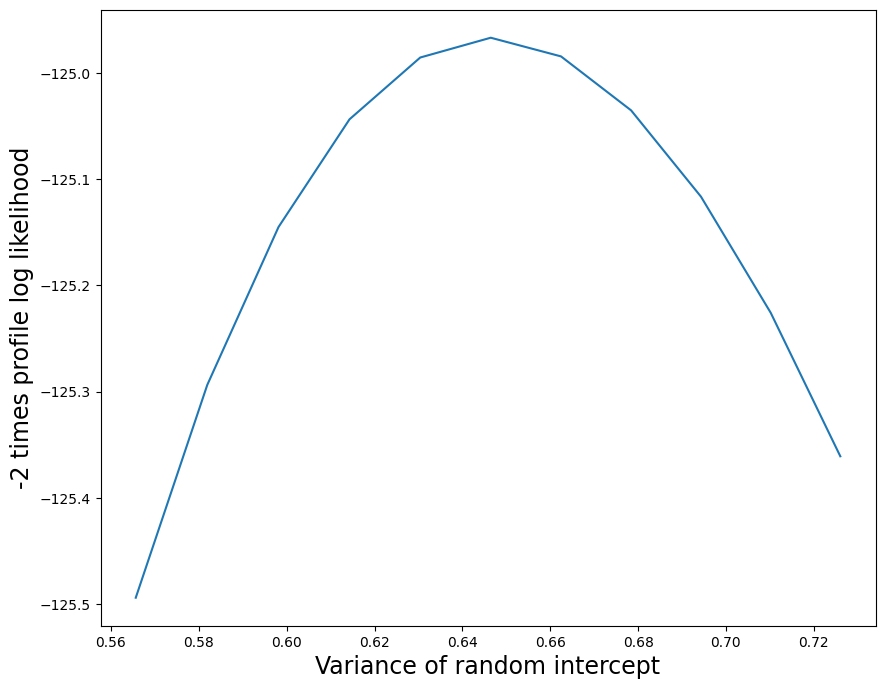
這是輪廓概似函式的圖。輪廓概似圖顯示隨機斜率變異數參數的 MLE 是一個非常小的正數,並且此估計值的不確定性很低。
[12]:
re = mdf.cov_re.iloc[1, 1]
with warnings.catch_warnings():
# Parameter is often on the boundary
warnings.simplefilter("ignore", ConvergenceWarning)
likev = mdf.profile_re(1, "re", dist_low=0.5 * re, dist_high=0.8 * re)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
plt.plot(likev[:, 0], 2 * likev[:, 1])
plt.xlabel("Variance of random slope", size=17)
lbl = plt.ylabel("-2 times profile log likelihood", size=17)